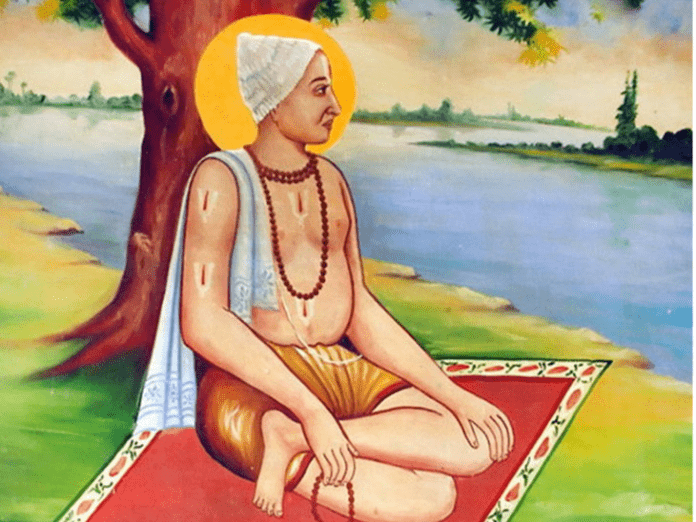
Before writing Ramacharitamanasa, Tulsidas had stored the story in his mind for a long time. Hence, this epic is also known as Tulsikrita Ramayana (Ramayana composed by Tulsidas). How much do you know about Ramacharita Manasa of Tulsidas..? Interesting facts about Ramcharita Manas are as follows.
The epic Ramacharitamanasa was written by Tulsidas in the 16th century in the period language, where Tulsidas is said to have adapted the original stories of the Ramayana for the eyes of new generations. Ramacaritamanasa is neither a word-for-word copy of Valmiki’s Ramayana nor an abridged commentary on the latter. Ramacharitamanasa contains elements from many other Ramayanas written earlier in Sanskrit and different Indian dialects and stories from Puranas. Tulsidas called the epic Ramacharitamanasa the story of Rama. It was stored in Shiva’s mind (Manasa). Later, he explained the same to his wife Devi Parvati. Tulsidas is said to have received the story through his guru, Naraharidasa. Before writing Ramacharitamanasa, Tulsidas had stored the story in his mind for a long time. Hence, the epic is also known as Tulsikrita Ramayana (Ramayana composed by Tulsidas). Ramacharitamanasa is a masterpiece of vernacular literature. Interesting things about Tulsidasa’s Ramacharita Manasa are as follows.
Ramayana and Ramacharitamanasa are different
Ramacharitamanasa and Ramayana are two different versions of the Rama story written in Sanskrit. Some differences can be seen between them in terms of style of poetry used, composition, religious significance and so on. Ramayana was written by sage Valmiki. It is considered to be the first book of Adi Kavya or Alankrita Kavya. Ramacaritamanasa is based on Valmiki’s original work. It was written by the great Awadhi poet Goswami Tulsi Das.
It is very important to note that Tulsidasa compares the seven kandas or adhyaya to the seven steps leading to Manasarovar. It is popularly believed that taking a bath in the Manasarovar near Mount Kailasa cleanses the mind and body by getting rid of all kinds of impurities.
Ramacharitamanasa is the Bible of North India
It is no exaggeration to say that Western scholars consider Ramacharitamanasa as the Bible of North India. Because the work is full of spiritual and religious thoughts. Mahatma Gandhi, the father of India, considered Tulsidas’s Ramayana more spiritual than Valmiki’s Ramayana.
Seven Kandas
Tulsidas wrote the work in seven Kandas and they are known as Bala Kanda, Ayodhya Kanda, Aranya Kanda, Kishkindakanda, Sundara Kanda, Lanka Kanda and Uttara Kanda. This is the main difference between Valmiki Ramayana and Ramacaritamanasa. Tulsidas did not write the sixth chapter under the title of Yuddha Kanda but titled it, Lanka Kanda. It is believed that Tulsidas abruptly ended the work of Ramacharitamanasa without going into the details of the events that took place in Uttarakhand as described by Valmiki.
Composition
The word Rama occurs 1443 times in Ramacharitamanasa. The word Sita appears 147 times and the word Janaki 69 times in Ramacharitamanasa. The word Vaidehi appears 51 times and temple 35 times. Similarly, the number of verses in Ramacaritamanasa is 27, the Chopai(dialect) number is 4608, and the Doha(couplet) number is 1074 in Ramacaritamanasa. Kishkindhakanda is the shortest chapter and Balakanda is the longest in this epic. Tulsidasari was 77 years old when Ramacharitamanasa was composed. Tulsidas started writing it in 1574 AD and completed it in 1576 after two years, seven months and 26 days. Tulsidas is also considered an avatar of Maharishi Valmiki. It is said that Lord Shiva inspired him to write Ramacharitamanasa in a dream.
Description
According to the Ramacharitamanasa, the speed of Pushpaka Vimana was 400 miles per hour, the battle between Rama’s team and Ravana’s team lasted for 87 days and the Rama-Ravana battle lasted for 32 days. Similarly, the bridge built to cross the ocean to reach Lanka took five days to complete. It is mentioned that Lord Rama stayed in Lanka for 111 days and Sita for 435 days.
The story of Surpanakhi
Vidyujihi was the husband of Ravana’s only sister Surpanakhi. For some reason Ravana killed Vidyujihi. Hurt, she curses in her mind that Ravana will die because of a woman. After becoming a widow, Shurpanakhi became a tyrant, so on the order of Sri Ramachandra, Lakshmana is said to have cut off her nose.
The reality of Ravana
Everyone knows that Ravana is the king of Lanka. But few people know that the real king of Lanka was Ravana’s half-brother Kuvera. According to Ramacharitamanasa, Kuvera was also a devotee of Lord Shiva. Pleased with his penance, Shiva gave him Lanka, after which Ravana won the battle with Kuvera. Ravana was also a great devotee of Lord Shiva. Ravana offered his head to Shiva as a sign of his severe penance. Because of this Shiva gave Ravana ten heads. That is why Ravana is also known as Darshana (the one with ten heads).
Sri Ram also had a sister
These four brothers Rama, Lakshmana, Bharata and Shatrughan also had an elder sister named Shanta. King Drupada had no children, so King Dasharatha gave him his daughter Shanta.
The story of Meghnath
Meghnath was the son of Ravana, and he was blessed with the boon of being killed by one who had not slept for 14 years. Lakshmana did not sleep for 14 years during his exile, hence he is also named Gudakesha. So Meghnath was killed by Lakshmana.
Vision of Tulsidas
Tulsidas is said to have had direct visions of Lord Hanuman, Lord Rama-Lakshmana and Shiva-Parvati in many of his works. During his travels, Tulsidas found a saint in Kashi who told him the address of Hanuman. After seeing Hanuman, he was blessed to have a glimpse of Lord Rama. But, when Lord Rama gave him darshan, Tulsidas could not recognize him. On the day of Mauni Amavasya, Lord Rama once again visited Tulsidasa and this time Hanuman helped him recognize Rama.